

The organ is used to view the outer world for the organism, but structurally, they are both different. A potato is simply a modified stem that also performs the function of storing starch for the plant. Sweet potato is a modified root that performs the function of storing starch for the plants.

These plant parts are nothing but storage forms of starch and plant products, but anatomically, both are different from one another. In bats, the wings are simply the folded skin of their fingers. The wings of insects are nothing but the extension of the integuments, which is the outermost layer of any animal that protects the body. In birds, the wing structure is formed of bones covered with feathers.
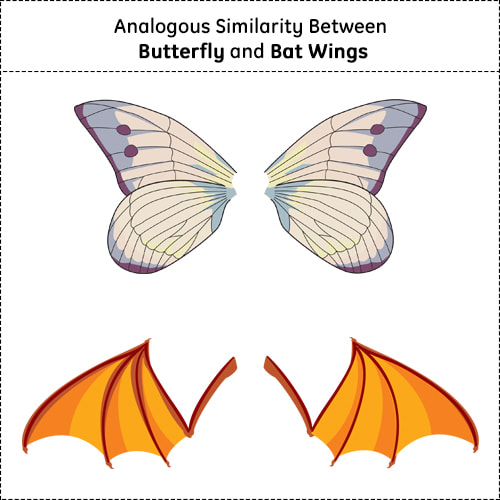
This organ presents the three different organisms that perform the same flying function but are different in structure. Examples of Analogous Organs Wings of Bats, Birds and Butterflies Generally, organisms that grow to have analogous organs do not share any common ancestor. The analogous organs belong to different, unrelated species, and due to evolutionary changes, the structures of the unrelated species develop in a certain way independently to perform similar types of functions. In terms of cladistics, the biological classification of the convergent evolution phenomenon is homoplasy. Convergent evolution is a form of evolution where other species evolve independently to develop to achieve a similar type of function. They are involved in convergent evolution. Analogous OrgansĪnalogous organs are the organs that are different anatomically in structure but perform the same function.

Examples of analogous organs are the wings of insects, birds, etc., which perform the same function of flying but are anatomically distinct from one another. Analogous organs and homologous organs also play an essential role in the evolution of species as both types are involved in different kinds of development. Homologous organs are the organs that are structurally similar to each other but perform different functions. Opposite of analogous organs are homologous organs. If any two structures or organs perform similar functions but are structurally different, they are analogous structures or analogous organs. Analogous organs are also termed analogues. Analogy means similarity between 2 things.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
